Exploring the Potential Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
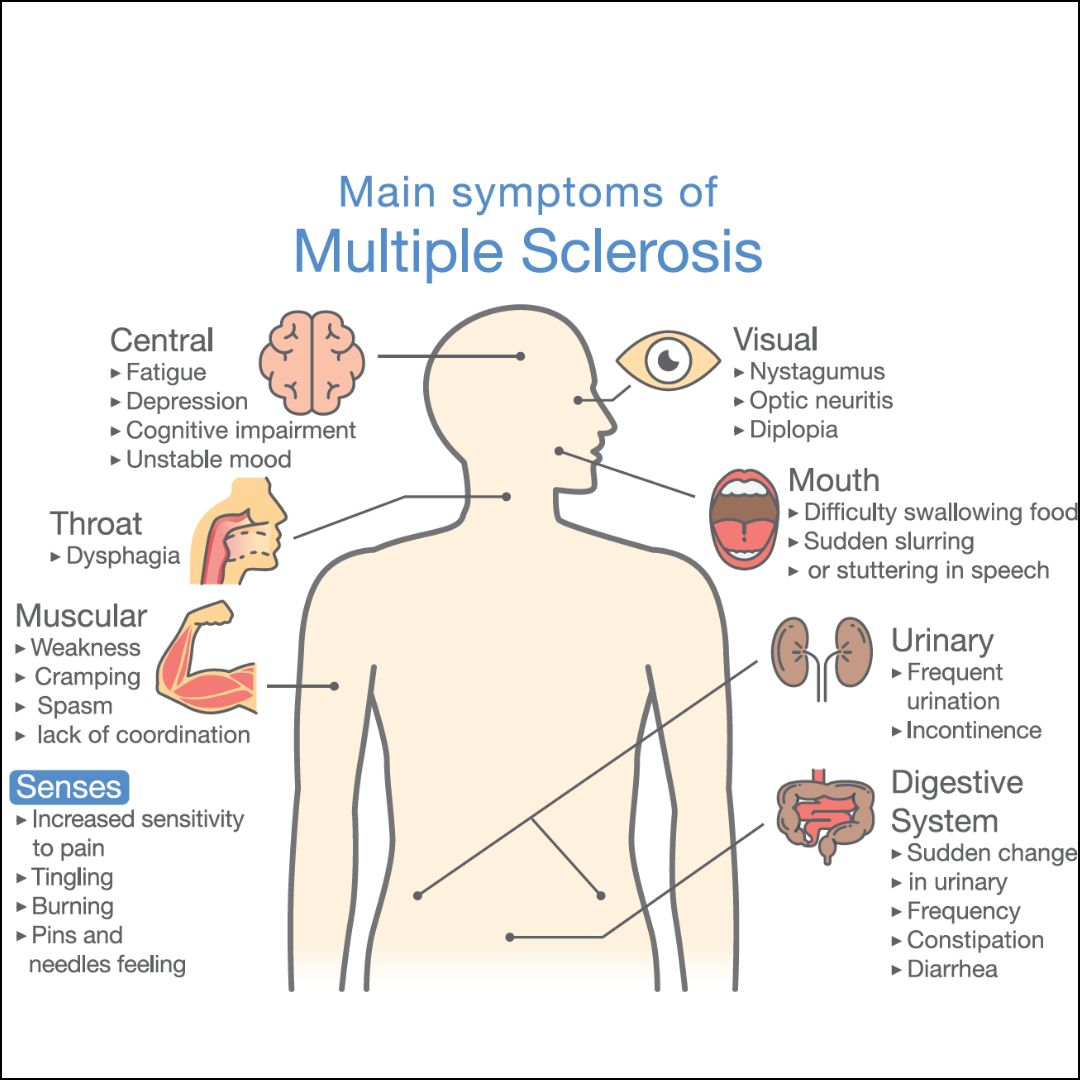
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neurological condition characterized by inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath, the protective covering of nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This damage disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to a variety of symptoms including fatigue, mobility issues, and cognitive impairment. While there is no cure for MS, various treatments aim to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. One such treatment that has gained attention is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT).
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?HBOT involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment, typically a hyperbaric chamber. This process increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the blood, which can enhance oxygen delivery to tissues, promote healing, reduce inflammation, and combat infection. Originally used to treat decompression sickness in divers, HBOT is now being explored for a wide range of medical conditions, including MS.
How Might HBOT Help with MS?The potential benefits of HBOT for MS patients stem from its ability to increase oxygen levels in the brain and spinal cord, where MS-related damage occurs. By improving oxygenation, HBOT may help to:
- Reduce Inflammation: In MS, the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath, leading to inflammation. HBOT’s anti-inflammatory effects could help mitigate this immune response, potentially slowing the progression of the disease.
- Promote Nerve Repair: Oxygen is vital for cellular repair and regeneration. HBOT may enhance the body's ability to repair damaged nerves, potentially improving symptoms related to nerve damage, such as mobility issues and neuropathic pain.
- Enhance Quality of Life: MS can significantly impact a patient's quality of life due to fatigue, pain, and other debilitating symptoms. Some studies suggest that HBOT may help alleviate these symptoms, leading to improved daily functioning and well-being.
- Potential Neuroprotective Effects: There is emerging evidence that HBOT might have neuroprotective properties, which could help preserve nerve function in individuals with MS, possibly slowing disease progression.
Current Research and Considerations
While there is promising evidence regarding the use of HBOT for MS, the research is still in its early stages, and results have been mixed. Some studies report significant benefits, while others show minimal to no effect. The variability in results may be due to differences in treatment protocols, such as the number of sessions, pressure levels, and patient selection.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy presents an intriguing potential treatment for Multiple Sclerosis, offering benefits such as reduced inflammation, enhanced nerve repair, and improved quality of life. However, more research is needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety in this context. Patients interested in HBOT should consult with their healthcare provider to weigh the potential benefits and risks in their specific case.
